Breeding the American Bully, like breeding any dog, is a significant responsibility and requires a deep understanding of the breed, its health issues, genetics, and the ethics of breeding. Here’s a comprehensive look at the process and considerations:
10 Things to Consider When Breeding
1. Understand the Breed Standard: Before breeding, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the American Bully breed standard. This standard provides guidelines on the ideal appearance, temperament, and other breed-specific traits. Breeding should aim to produce puppies that adhere to this standard.
2. Health Screenings: Before mating, both the male and female should undergo thorough health screenings to ensure they don’t have any hereditary or genetic disorders that could be passed on to the offspring. Common screenings include checks for hip dysplasia, heart conditions, and other breed-specific health issues.
3. Genetic Testing: Modern technology allows breeders to test dogs for potential genetic issues. This can help in making informed decisions about which dogs to breed to ensure healthy litters.
4. Selecting a Mate: Choosing a suitable mate for your dog is crucial. Look for a dog that complements your own in terms of genetics, temperament, and conformation. This might involve researching pedigrees and possibly traveling to find the right match.
5. Ethical Considerations: Only breed if you’re committed to finding loving homes for all the puppies. Avoid overbreeding, which can lead to health issues for the female and contribute to overpopulation.
6. Pregnancy and Whelping: Once the female is pregnant, she’ll need special care, including a proper diet, regular vet check-ups, and a safe place to give birth. Be prepared for potential complications and have a vet on call.
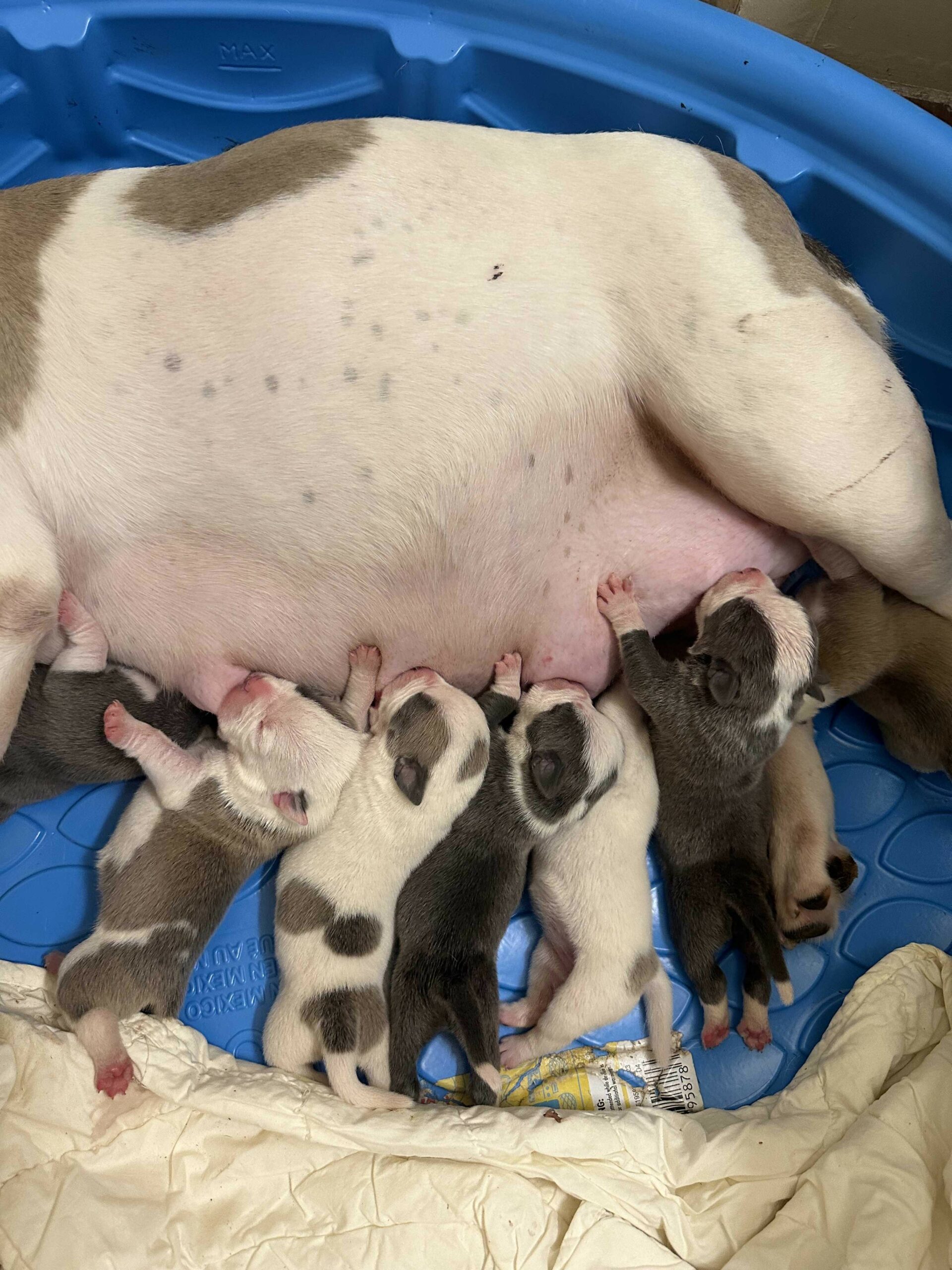
7. Raising Puppies: The first few weeks of a puppy’s life are crucial. They’ll need to be fed, kept warm, and monitored for any signs of health issues. As they grow, socialization and early training are vital to ensure they develop into well-adjusted adults.
8. Finding Homes: Before breeding, consider whether you have the resources and network to find loving homes for all the puppies. This might involve interviews, home checks, and ensuring new owners are prepared for the responsibility of dog ownership.
9. Lifelong Commitment: Ethical breeders commit to the puppies they produce for their entire lives. This means being available for questions, taking back dogs if necessary, and ensuring the well-being of every puppy, even once they’ve left your care.
10. Continuous Learning: The world of dog breeding is complex, and there’s always more to learn. Whether it’s new health screenings, changes to the breed standard, or advances in genetics, committed breeders stay informed.
The Breeding Process
The breeding process can be broken down into several stages, each with its own set of considerations and challenges:
1. Pre-Breeding Preparation:
- Research and Education: Understand the breed standard, genetics, and potential health issues. Join breed clubs and attend seminars to gain knowledge.
- Health Screenings: Ensure both potential breeding dogs are screened for common genetic disorders and health issues specific to the breed.
- Selecting Breeding Pairs: Choose dogs that complement each other in terms of genetics, temperament, and conformation.
2. Estrus and Mating:
- Estrus Cycle: Female dogs typically come into heat twice a year. Recognize the signs of estrus, such as swelling of the vulva and bloody discharge.
- Optimal Mating Time: Utilize progesterone testing to determine the best time for mating, usually around the 10th to 14th day of the cycle.
- Natural Mating or Artificial Insemination: Depending on circumstances, breeders might choose natural mating or opt for artificial methods.
3. Pregnancy:
- Confirmation: Pregnancy can be confirmed through methods like palpation, ultrasound, or blood tests.
- Prenatal Care: Ensure the pregnant female receives proper nutrition, regular vet check-ups, and a safe environment.
- Preparation for Whelping: Set up a quiet and comfortable whelping box where the female can give birth.
4. Whelping (Birth):
- Signs of Labor: Look for signs like restlessness, nesting behavior, and a drop in body temperature.
- Assisting in Birth: While many dogs give birth without complications, be prepared to assist if necessary and have a vet on standby.
- Post-Birth Care: Ensure all puppies are breathing, nursing, and are kept warm.
Common Breeding Complications
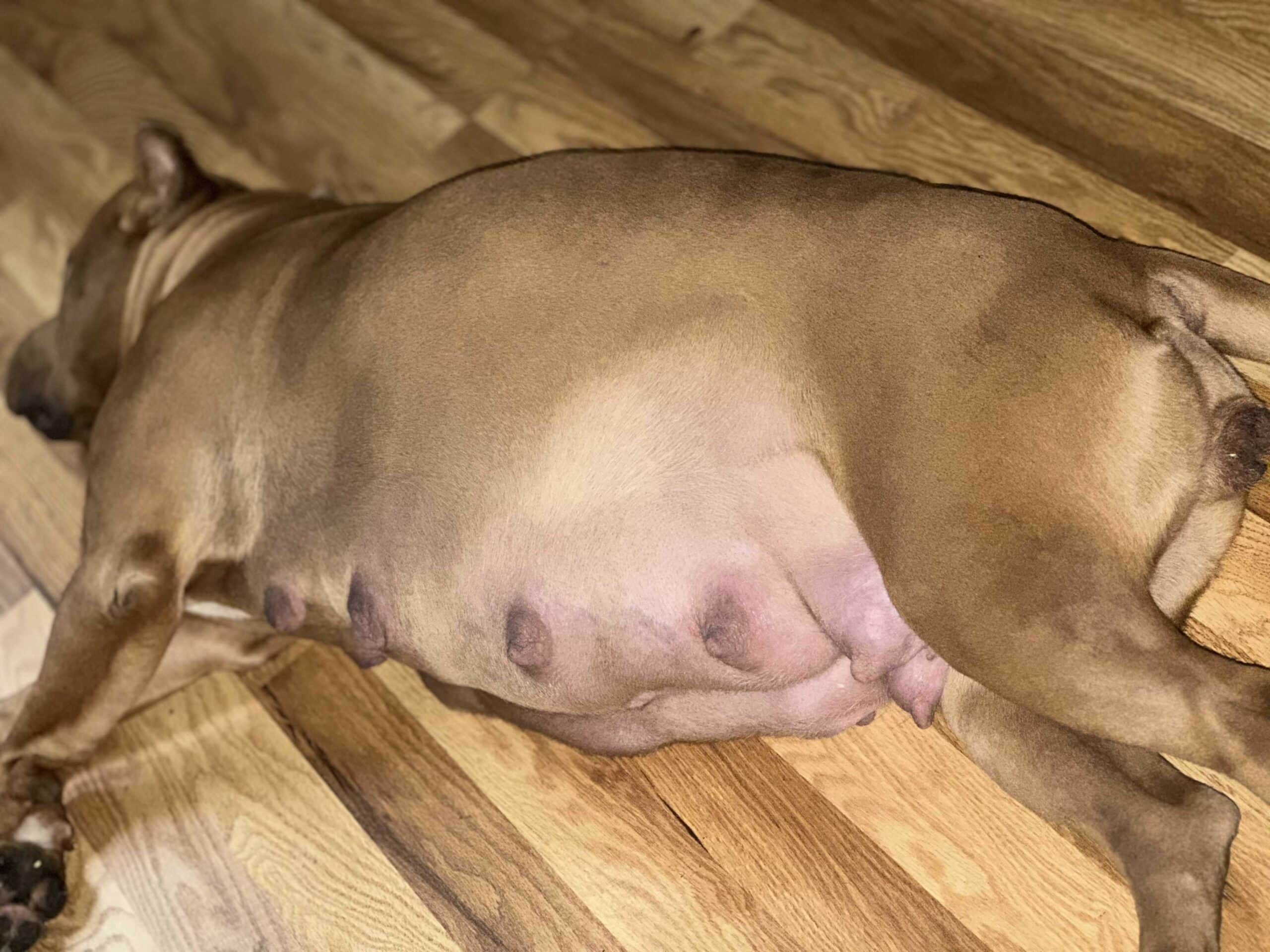
Breeding dogs, including the American Bully, can come with a range of complications. These complications can arise at any stage of the breeding process, from mating to pregnancy to whelping. It’s essential for breeders to be aware of these potential issues to ensure the health and safety of both the mother and her puppies. Here’s a detailed look at some common breeding complications:
1. Mating Difficulties:
- Failure to Mate: Some dogs may be reluctant or unable to mate due to behavioral issues, inexperience, or physical problems.
- Injuries: Dogs can sometimes injure each other during the mating process, especially if one of them becomes aggressive or if they’re not properly supervised.
2. Fertility Issues:
- Infertility: Both male and female dogs can face fertility issues, making it difficult to produce a litter.
- Low Sperm Count: Males might have a low sperm count, which can reduce the chances of successful impregnation.
- Irregular Estrus Cycles: Some females might not come into heat regularly, making timing for mating challenging.
3. Pregnancy Complications:
- Miscarriage: Also known as spontaneous abortion, this is when a pregnant dog loses her puppies during gestation.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: This rare condition occurs when the embryo implants outside the uterus.
- Gestational Diabetes: Some pregnant dogs might develop diabetes, requiring careful monitoring and treatment.
4. Whelping Difficulties:
- Dystocia: This is when a dog has difficulty giving birth. It can be due to oversized puppies, a small birth canal, or weak uterine contractions.
- Retained Placenta: If the placenta isn’t expelled after the birth of a puppy, it can lead to infections.
- Stillbirth: Sometimes, puppies are born dead due to various reasons, including developmental abnormalities or complications during birth.
- Inadequate Milk Production: Some mothers might not produce enough milk to feed all their puppies, requiring supplemental feeding.
5. Post-Whelping Issues:
- Mastitis: This painful infection of the mammary glands can occur if bacteria enter through cracked nipples.
- Metritis: An inflammation of the uterus that can occur after giving birth, often due to retained placental fragments or a bacterial infection.
- Eclampsia: Also known as milk fever, this is a life-threatening condition caused by low blood calcium levels in nursing mothers.
6. Puppy Complications:
- Fading Puppy Syndrome: Some puppies, despite appearing healthy at birth, weaken and die within the first few weeks. The exact cause can be hard to determine.
- Congenital Defects: Puppies might be born with birth defects, which can be due to genetic factors or issues during pregnancy.
- Infections: Newborn puppies are vulnerable to various infections, especially if the birthing environment isn’t clean.
Conclusion: Breeding American Bullies, or any dog, is not a task to be taken lightly. It requires dedication, knowledge, and a genuine love for the breed. If done responsibly, it can be a rewarding experience that contributes positively to the breed’s future. However, if done without proper knowledge or for the wrong reasons (like just making money), it can lead to health issues, overpopulation, and suffering for the dogs involved.